Deploy to prod using a git workflow
Windmill integration with Git repositories makes it possible to adopt a robust development process for your Windmill scripts, flows and apps.
This is the recommended way to deploy to prod in Windmill.
For all details on Deployments to prod in Windmill, see Deploy to prod.
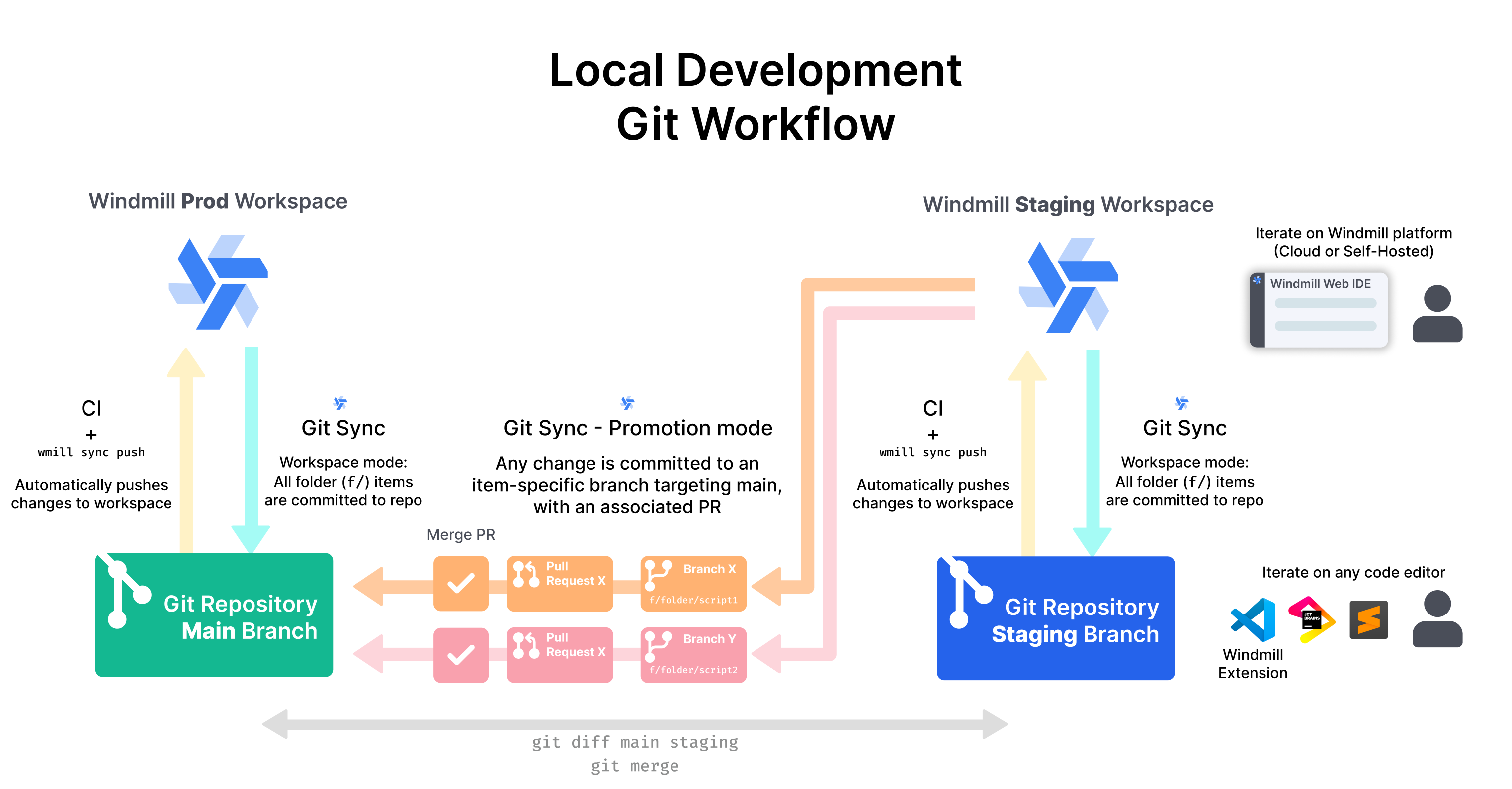
See section Setup the full Git workflow for the detailed setup steps.
The integration with git works in three-folds:
- GitHub Action + CLI: upon any commit to a particular branch, the GitHub action will run the
wmillCLI and push to a Windmill workspace this works using the CLI doingwmill sync push(free & open source).
You can also trigger a webhook and push the changes to Windmill using this Windmill script and pass the arguments as query args in the webhook triggered after pushing to the repo.
-
Git sync (Sync mode): Windmill automatically committing to a git repository upon any deployment to a workspace, this works using the CLI doing
wmill sync pull(Cloud and Enterprise Self-Hosted). Having it commit back to Windmill has 2 benefits:- It ensures that any automatically created metadata files are wrote-back (in case you pushed a script without its metadata for instance).
- It ensures that any modification done in the UI is kept in sync with the git repository and guarantees a bi-sync between the repo and the UI.
-
Git sync (Promotion mode): Windmill automatically creates a branch specific to that item (and whose name is derived from that item) that targets the branch set in the git sync settings, upon any change to any items, be it from the UI or from git (Cloud and Enterprise Self-Hosted). This should be coupled with a GitHub action that automatically create a PR when a branch is created. This PR can then be reviewed and merged. Upon being merged to the prod branch, a GitHub action as described in 1. would then deploy it to the prod branch.
Once everything is set up, the process is as follows:
- Users iterate and make their changes in the "staging" Windmill workspace UI or in the git staging branch directly.
- Every time a Windmill App, Flow or Script is deployed to that workspace (via Windmill's UI or through the GitHub action that deploys to staging upon any change), Windmill automatically sync it back to the repo on the "staging" branch (Git sync - sync mode) and also create a branch that targets prod and keep it in sync with any new changes (Git sync - Promotion mode)
- On every new branch created, PRs are automatically created via a GitHub Action. Approved GitHub users can review and merge those PRs.
- Every time a PR is merged, another GitHub Action automatically deploys the change to a "production" Windmill workspace.
Note that although the CLI is used by both the GitHub Action and the Git sync, the CLI does not need to be used directly by any users and everything happen behind the scene in an automated way.
This gives the flexibility to fully test new Windmill scripts, flows and apps, while having them version-controlled and deployed in an automated way to the production environment.
This process can be used in particular for local development.
Check out the windmill-sync-example repository as an illustration of this process.
Deploying to a prod workspace using git requires the Git sync feature, which is is a Cloud plans and Self-Hosted Enterprise Edition-only feature.
From the workspace settings, you can set a git_repository resource on which the workspace will automatically commit and push scripts, flows and apps to the repository on each deploy.
Setup the full Git workflow
Note: this is the detailed setup steps for a GitHub repository. It will need to be adapted for GitLab.
The video below shows a simplified setup, see the steps below it for the full setup.
If you are not using the Enterprise Edition (EE) version of Windmill, you can still follow the parts of this guide that do not involve Git sync.
The guide covers a staging and prod setup. To add an additional dev environment, simply consider staging to be the target of the dev workspace and prod to be the target of the staging workspace.
Pull workspace locally
- Open your terminal and add your workspace to the Windmill CLI using the command:
wmill workspace add <workspace-name> <workspace-id> <url> - Authorize the CLI to access the workspace.
- Pull the entire Windmill workspace locally to your machine.
The CLI is able to sync variables, resources and secrets as well. However, everywhere the CLI is used here, it it set with the flags --skip-variables --skip-secrets --skip-resources to avoid syncing them. This is because variables, resources and secrets should have values that are specific to each environment.
For instance, a resource named f/myproject/myimportantdb should have a different value in staging and prod. This is why they are not synced and should be set manually in each environment. You can however if you prefer, manually sync those. Do note that secrets have an additional layer of encryption and are by default exported in their encrypted form whose decryption key is workspace specific. To sync them between workspace, use --plain-secrets to export them in plain text.
Push workspace to GitHub
- Create a new private repository on GitHub.
- Use the suggested Git commands to push your local repository to GitHub.
- Verify that your workspace is now available in the GitHub repository.
Setup git sync
- In Windmill, navigate to the workspace settings and go to the Git sync tab.
- Create a
git_repositoryresource with the necessary URL, username, repo name, and a GitHub token. You can also use a GitHub app installation to connect a repo to your windmill instance. - Generate a fine-grained GitHub token with read and write permissions for content and add it to the Windmill
git_repositoryresource.
Your URL should be https://[USERNAME]:[TOKEN]@github.com/[ORG|USER]/[REPO_NAME].git
If you do the setup with a staging workspace, you can set the branch to 'Staging'.
Test git sync:
- Create a folder in your Windmill workspace and add scripts, apps, and flows to it.
- Verify that these items are pushed to the GitHub repository and appear in the correct folder structure.
Deploy to a prod workspace using a git workflow
- Set up a new empty workspace in Windmill that will be the target of the prod branch.
- Enable the Create one branch per deployed object option in the Git sync settings.
- In GitHub, allow actions to create and approve pull requests.
- Create a user token in Windmill and save it as a secret named
WMILL_TOKENin your GitHub repository Settings > "Secret and Variable" > "Actions".
Test deploy to prod workspace:
- From the staging workspace, create a new flow and save it in a folder.
- Verify that a new branch is created in the GitHub repository and a pull request is opened.
- Merge the pull request and check that the changes are deployed to the prod workspace in Windmill.
GitHub Actions setup
- Add GitHub Actions to your repository. You will find the necessary actions in the windmill-sync-example repository.
- Create a
.github/workflowsdirectory in your repository and add the following files:open-pr-on-commit.yaml: This action automatically creates a PR when Windmill commits a change.push-on-merge.yaml: This action automatically pushes the content of the repo to the Windmill prod workspace when a PR is merged. Update theWMILL_WORKSPACEvariable to the name of your prod workspace.- Optionnaly, if you want to add a staging workspace, copy the previous GitHub action/workflow file but now set the
WMILL_WORKSPACEvariable to the id of the staging workspace and theWMILL_URLvariable to the base URL of the Windmill instance if different than the one for prod. Also changes the trigger to listen to the branches: 'staging'. push-on-merge-to-forks.yaml: This does the same aspush-on-merge.yamlbut for all Workspace Forks, enabling the full power of the feature.
On top of WMILL_TOKEN, 2 other variables need to be set in the GitHub action workflow file:
WMILL_WORKSPACE: the name of the workspaceWMILL_URL: the base URL of the Windmill instance (e.g. https://app.windmill.dev/)
- open-pr-on-commit.yaml
- push-on-merge.yaml
- push-on-merge-to-forks.yaml
name: Windmill Pull Request
on:
push:
branches:
- wm_deploy/github-sync-example-staging/**
- wm-fork/**
env:
TARGET_BRANCH: main
jobs:
submit_pull_requests:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
permissions:
contents: read
pull-requests: write
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Create pull request
run: |
gh pr view ${{ github.ref_name }} \
&& gh pr reopen ${{ github.ref_name }} \
|| gh pr create -B ${{ env.TARGET_BRANCH }} -H ${{ github.ref_name }} \
--title "${{github.event.head_commit.message }}" \
--body "PR created by Github action '${{ github.workflow }}'"
env:
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
name: "Push main to Windmill workspace"
on:
workflow_dispatch:
push:
branches:
- "main"
# if the windmill workspace is persisted in a subfolder of this repos, you can add the following to avoid pushing to windmill when there's no change
# paths:
# - wm/**
env:
WMILL_URL: https://app.windmill.dev/
WMILL_WORKSPACE: github-sync-example-prod
jobs:
sync:
environment: windmill
runs-on: "ubuntu-latest"
steps:
- name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 20
# We check the commit to make sure it doesn't start with [WM] which commits coming from Windmill Git Sync do.\
# If that's the case, then we stop the workflow as we want to avoid overwriting changes that are out-of-sync
# (for instance if one were to deploy in quick succession)
- name: Check commit message
id: check_message
run: |
COMMIT_MESSAGE="${{ github.event.head_commit.message }}"
if [[ "$COMMIT_MESSAGE" =~ ^\[WM\] ]]; then
echo "Commit message starts with '[WM]', skipping push to Windmill to avoid overwriting deploy that immediately follows it"
echo "skip=skip" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
fi
# (push will pull first to detect conflicts and only push actual changes)
- name: Push changes
if: steps.check_message.outputs.skip != 'skip'
run: |
npm install -g [email protected]
wmill sync push --yes --skip-variables --skip-secrets --skip-resources --workspace ${{ env.WMILL_WORKSPACE }} --token ${{ secrets.WMILL_TOKEN }} --base-url ${{ env.WMILL_URL }}
name: "Push forks to Windmill workspace forks"
on:
workflow_dispatch:
push:
branches:
- wm-fork/**
# if the windmill workspace is persisted in a subfolder of this repos, you can add the following to avoid pushing to windmill when there's no change
# paths:
# - wm/**
env:
WMILL_URL: https://app.windmill.dev/
jobs:
sync:
environment: windmill
runs-on: "ubuntu-latest"
steps: - name: Checkout
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 20
- name: Extract workspace from branch name
id: workspace
run: |
BRANCH_NAME=${GITHUB_REF#refs/heads/}
WORKSPACE=$(echo "$BRANCH_NAME" | sed 's|wm-fork/|wm-fork-|' | sed 's|/|-|g')
echo "workspace=$WORKSPACE" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
# We check the commit to make sure it doesn't start with [WM] which commits coming from Windmill Git Sync do.\
# If that's the case, then we stop the workflow as we want to avoid overwriting changes that are out-of-sync
# (for instance if one were to deploy in quick succession)
- name: Check commit message
id: check_message
run: |
COMMIT_MESSAGE="${{ github.event.head_commit.message }}"
if [[ "$COMMIT_MESSAGE" =~ ^\[WM\] ]]; then
echo "Commit message starts with '[WM]', skipping push to Windmill to avoid overwriting deploy that immediately follows it"
echo "skip=skip" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
fi
# (push will pull first to detect conflicts and only push actual changes)
- name: Push changes
if: steps.check_message.outputs.skip != 'skip'
run: |
npm install -g [email protected]
wmill sync push --yes --skip-variables --skip-secrets --skip-resources --workspace ${{ steps.workspace.outputs.workspace }} --token ${{ secrets.WMILL_TOKEN }} --base-url ${{ env.WMILL_URL }}
Testing
You are now ready to test the workflow. You can do so by:
- Create and deploy a new script in the staging workspace, give it a path within the allowed filters.
- Verify in the GitHub action run that the sync push has been able to push the change to the staging workspace (or the prod workspace if you have not set up a staging workspace).
- Check the target workspace in Windmill if the script has been deployed.
- Go to the runs page, toggle the "Sync" kind of jobs. You should see at least 2 jobs, one to push back your change to the staging (if set) workspace (no-op), and one to create a branch that targets the main branch (the one that will be merged).
- Now in your repository, you should see a new branch named wm_deploy/[WORKSPACE_NAME]/[SCRIPT_PATH] (for instance wm_deploy/staging/f/example/script).
- Merge that branch, now the changes should trigger the "Deploy to prod" GitHub action in the main branch.
Managing multiple teams and folders
When working with multiple teams in Windmill, there are several approaches to organize your workflows and prevent overlapping changes. Here are the recommended practices:
Option 1: Same workspace, different folders, different repositories
This is the recommended approach for most cases:
- Keep all teams in the same workspace but assign each team to different folders
- Create separate repositories for each team
- In each repository's
wmill.yaml, specify the folders that team has ownership of using theincludesfield:
includes:
- "f/team1_folder/**" # Team 1's folder
- "f/team2_folder/**" # Team 2's folder
This setup ensures that:
- Each team works in their own isolated space.
- Changes from different teams won't overlap.
- Teams can have the same initial code in their respective folders.
- Each team's changes will be tracked in their own repository.
Option 2: Separate workspaces
Alternatively, you can create separate workspaces for each team. This approach:
- Provides complete isolation between teams.
- Allows teams to have their own deployment workflows.
- May require more maintenance overhead.
- Is useful when teams need completely different configurations or environments.
Managing changes and pull requests
When using the promotion mode in Git sync:
- Changes to the same item will be grouped into a single PR.
- Different items will create separate PRs.
- You can use the group per folder option to group changes by folder instead of by item.
When setting up multiple repositories for different teams, ensure that each repository's wmill.yaml file correctly specifies the folders the team should have access to. This prevents accidental modifications to another team's code.