Welcome to the second day of Windmill's first launch week. To follow all the announcements made this week, please go to the Launch Week #1 page.
Today we are unveiling features related to workers. Workers are the foundation of Windmill. They are autonomous processes that run one script at a time using the entire CPU and memory available to them.
We are proud to announce:
- Worker groups to share configurations between workers, assign them to listen to particular queues of jobs (and optionally assign priorities) or change their pre-installed binaries on the fly (this article).
- Dedicated workers for scripts.
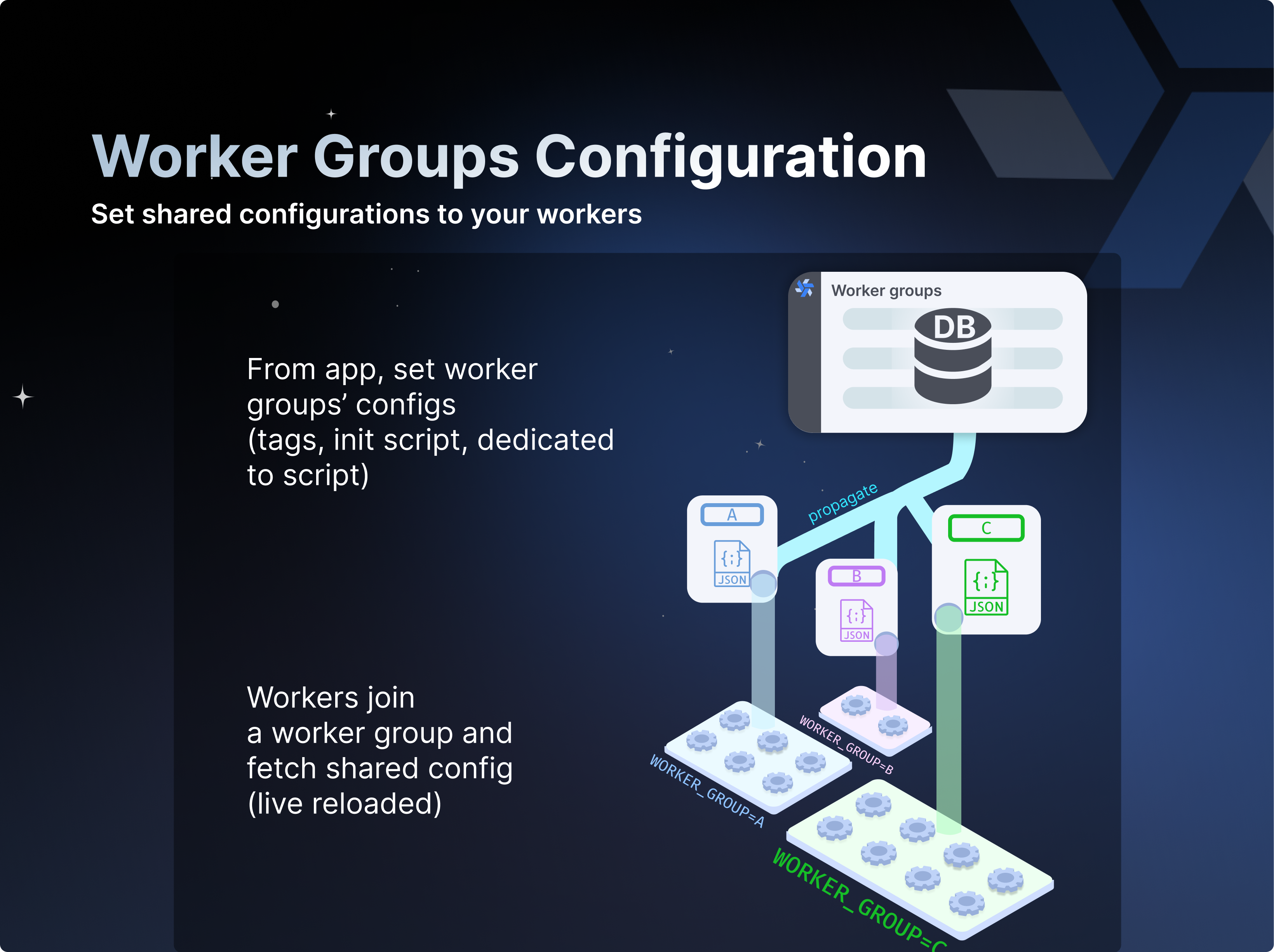
Worker groups are managed from the UI and are hot reloaded.
What is the purpose of worker groups?
In Windmill, workers run the jobs. The number of workers can be horizontally scaled up or down depending on needs without any overhead. Each worker on Windmill can run up to 26 million jobs a month, where each job lasts approximatively 100ms.
By default, every worker is the same and interchangeable. However, there are often needs to assign jobs to a specific worker pool, and to configure this worker pool to behave specifically or have different pre-installed binaries. To that end, we introduce the concept of "worker groups".
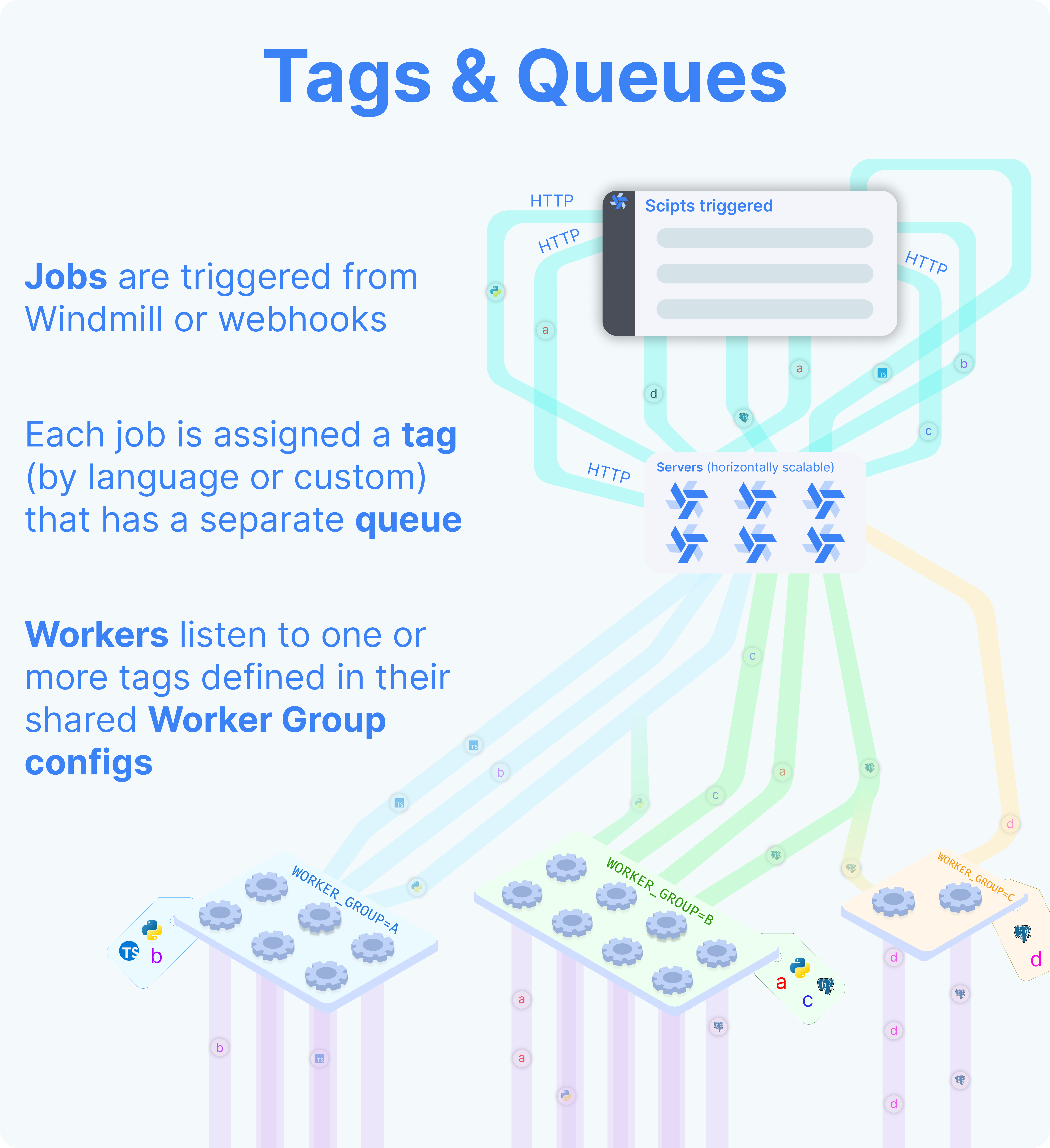
You can assign groups to flows and flow steps to be executed on specific queues. The name of those queues are called tags. Worker groups listen to those tags.
Examples of configurations include:
- Assign different jobs to specific worker groups by giving them tags.
- Set an init script that will run at the start of the workers (e.g. to pre-install binaries).
- Dedicate your worker to a specific script or flow for high throughput.
Once the configurations are done in the Windmill UI, the workers take their configuration dynamically, without having to manually restart them.
How to have a Worker join a Worker Group
Create a worker group in your docker-compose.yml and simply pass the worker group as the env variable WORKER_GROUP=<name_of_worker_group> for it to automatically join its corresponding worker group.
Windmill's responsibility is not to spawn the worker itself but to play well with existing service orchestrator such as Kubernetes, ECS, Nomad or Docker Compose, and any IaC. In those, you define the number of replicas (which can be auto-scaled up or down), the resource to allocate to those workers and the WORKER_GROUP passed as env.
Upon start, those workers will automatically join their worker group and fetch their configurations (including init scripts). They will also listen for changes on the worker group configuration for hot reloading.
Here is an example of a worker group specification in docker-compose:
windmill_worker_highmem:
image: ghcr.io/windmill-labs/windmill-ee:main
pull_policy: always
deploy:
replicas: 2
resources:
limits:
cpus: '1'
memory: 4096M
restart: unless-stopped
environment:
- DATABASE_URL=${DATABASE_URL}
- MODE=worker
- WORKER_GROUP=highmem
Assign replicas, resource constraints, and that's it, the worker will automatically join the worker group on start and be displayed on the Workers page in the Windmill app!
Worker only require a database URL and can thus be spawned in separate VPCs if needed (as long as there is a tunnel to the database). There is also an agent mode for situations where workers are running in an untrusted environment.
Assign different jobs to specific worker groups
Giving tags to workers will change their behavior to only pull and execute jobs with those tags from the queue. When writing a script that should be executed on a specific worker group, you have to add at least one tag the worker group is listening for.
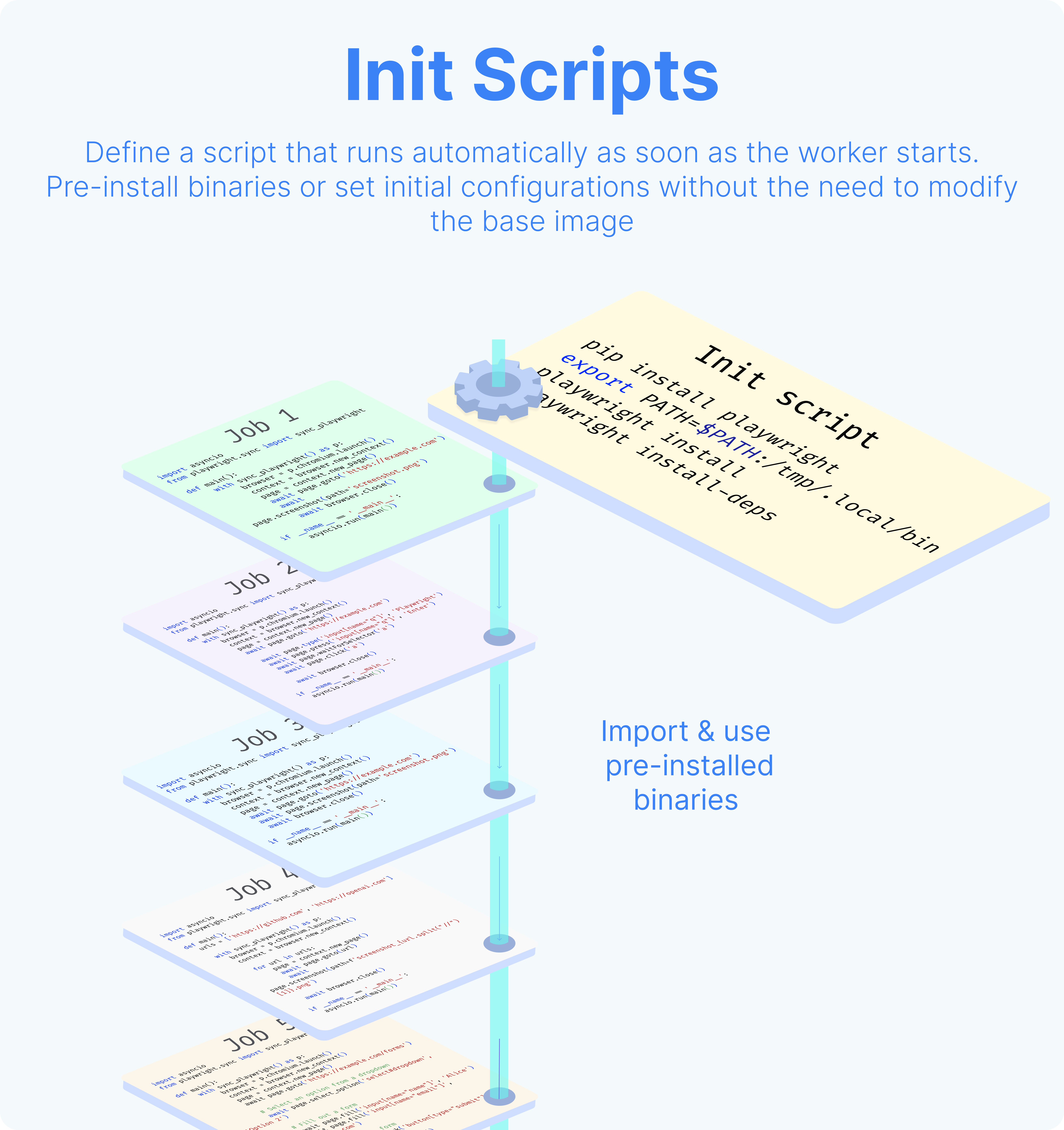
Set an init script
Setting an init script to a worker group configuration will automatically trigger a Bash script every time the workers are started. This approach offers added convenience to pre-install binaries or set initial configurations without the need to modify the base image.
Dedicate your worker to a specific script or flow
Dedicated Workers are workers (groups) that are dedicated to a particular script or flow. We've written another blog post dedicated to this here.
How to create worker group configurations
In a self-hosted instance, worker groups are created from your docker-compose.yml by simply passing the worker group as the env variable WORKER_GROUP=worker_group_name.
It is as simple as that and means that workers can be scaled horizontally.
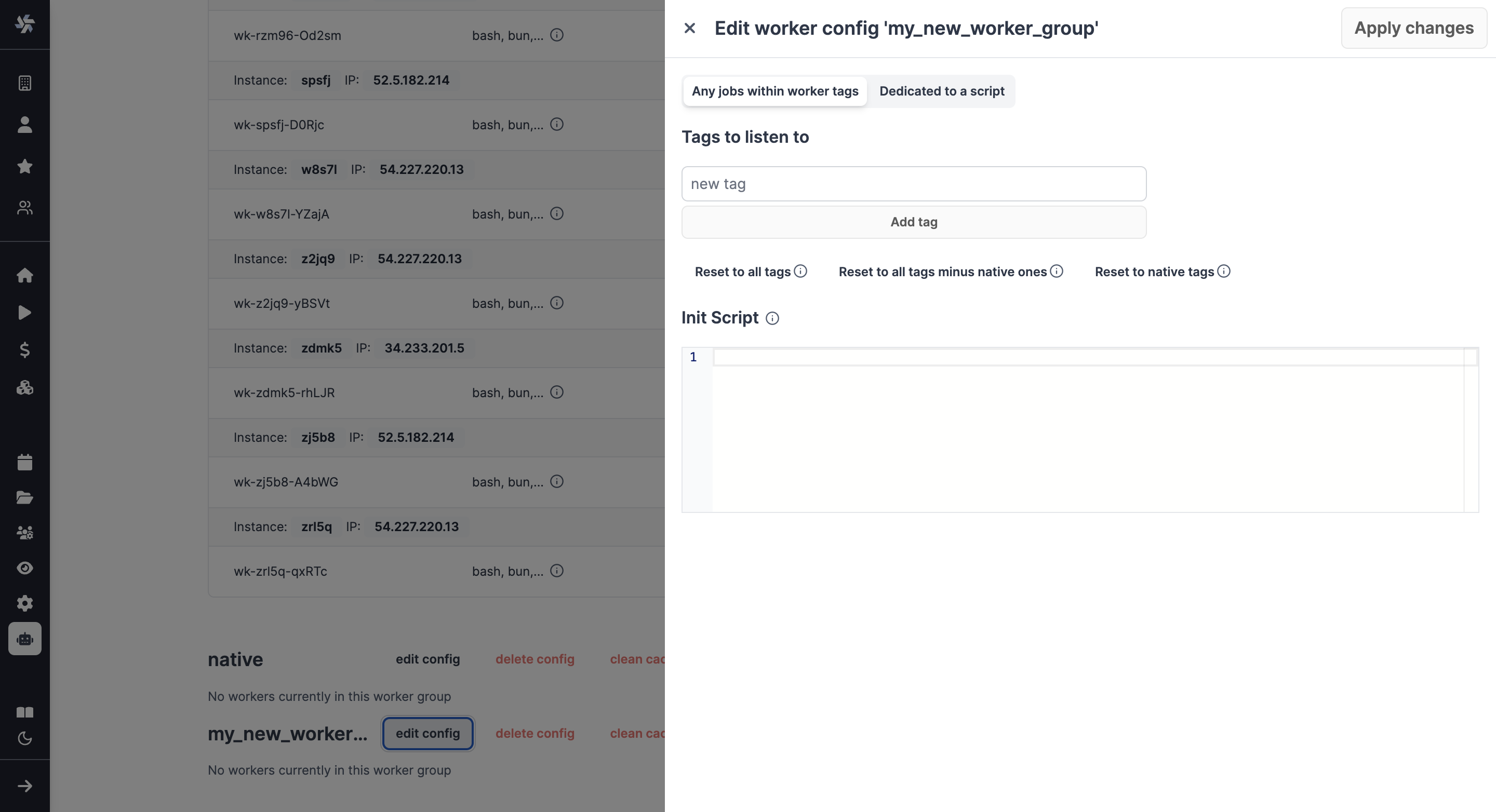
The configuration of worker groups is done from the Windmill UI's Workers page, pick "New worker group config" and just write the name of your worker group.
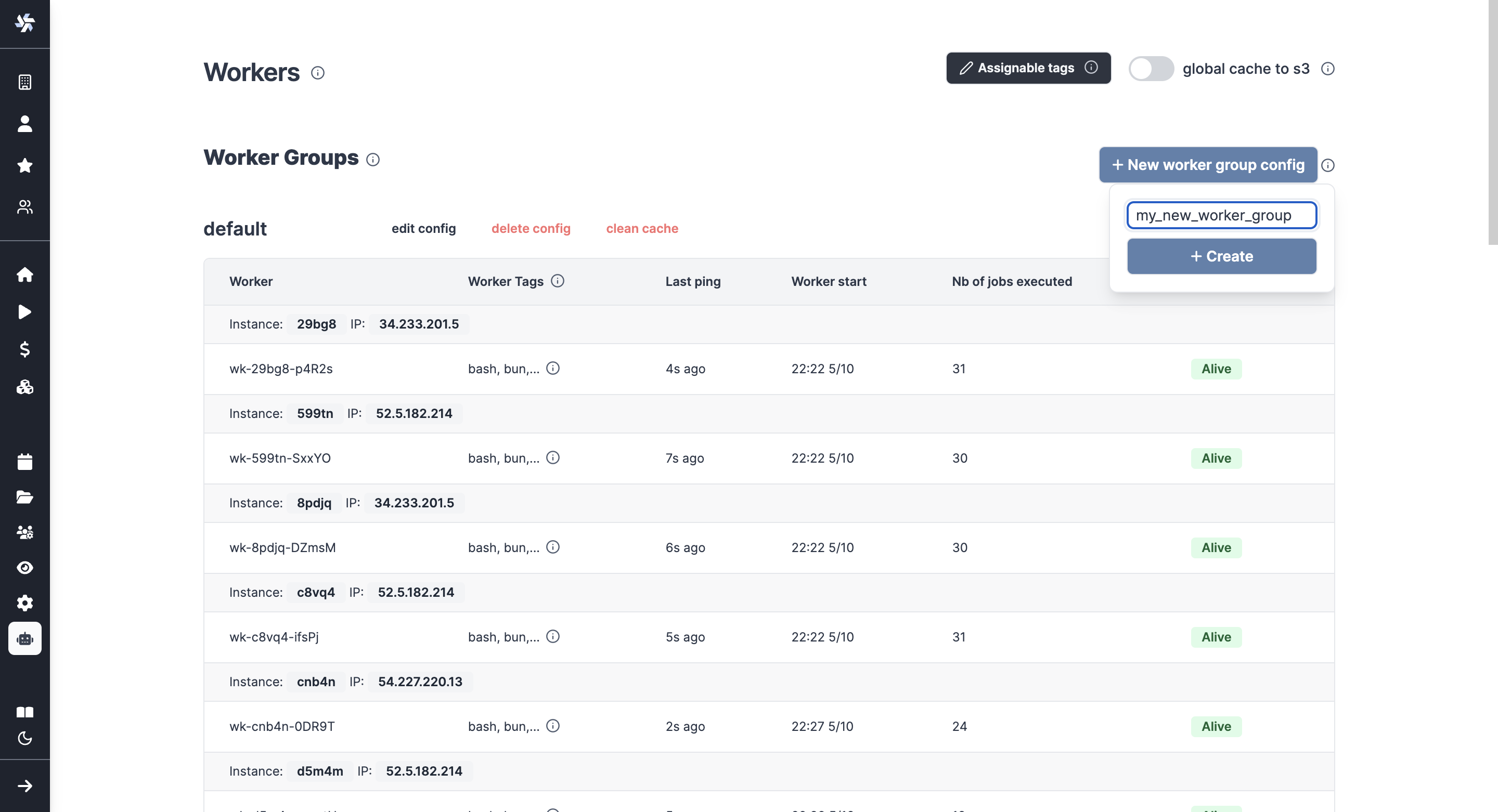
You can then configure it directly from the UI and in particular set tags to listen to, define an init script or dedicate it to a script.
Learn more
You can self-host Windmill using a
docker compose up, or go with the cloud app.